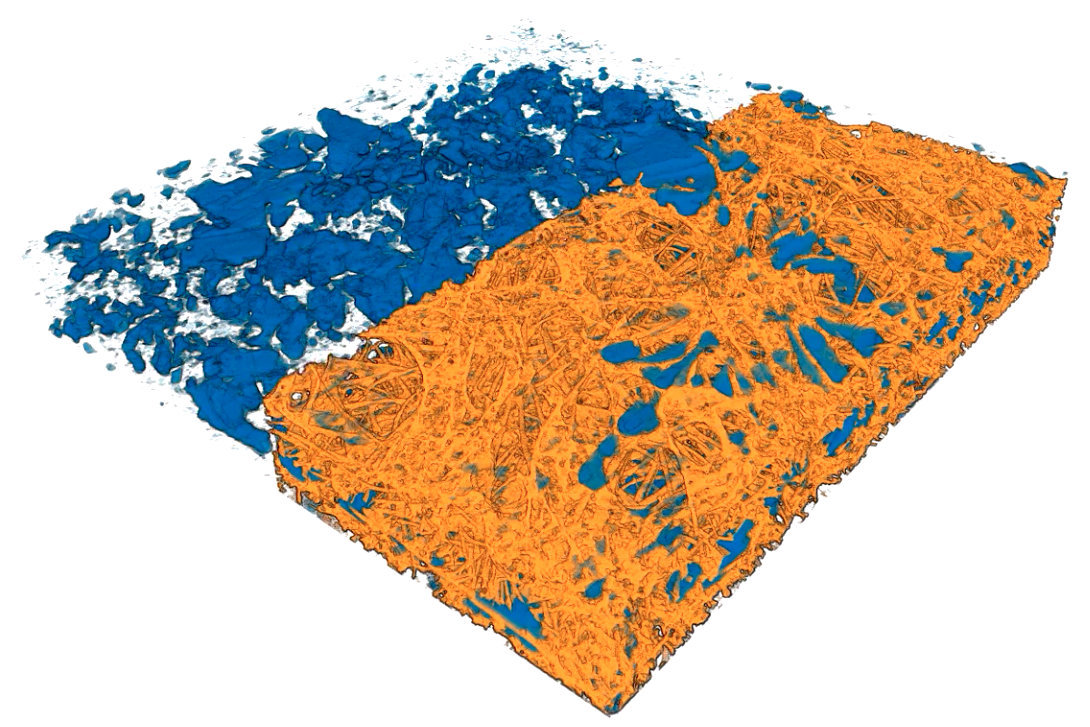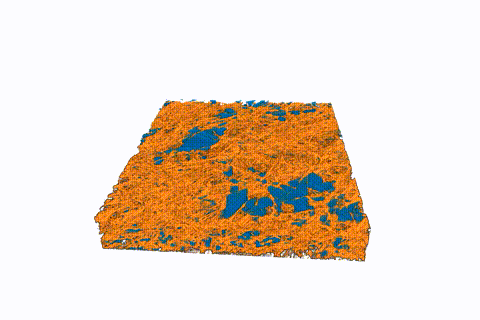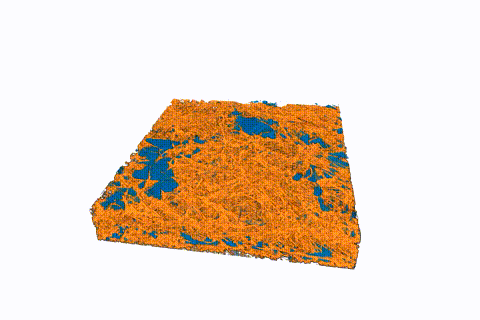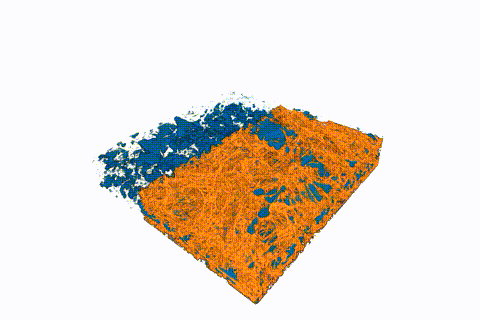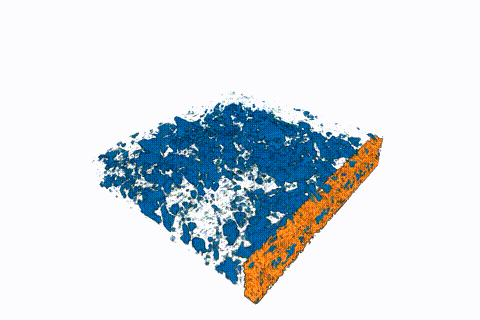
This animated 3-D rendering (view larger size), generated by an X-ray-based imaging technique at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source, shows tiny pockets of water (blue) in a fibrous sample. The X-ray experiments showed how moisture and temperature can affect hydrogen fuel-cell performance. (Credit: Berkeley Lab)
Like a well-tended greenhouse garden, a specialized type of hydrogen fuel cell – which shows promise as a clean, renewable next-generation power source for vehicles and other uses – requires precise temperature and moisture controls to be at its best. If the internal conditions are too dry or too wet, the fuel cell won’t function well.
But seeing inside a working fuel cell at the tiny scales relevant to a fuel cell’s chemistry and physics is challenging, so scientists used X-ray-based imaging techniques at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and Argonne National Laboratory to study the inner workings of fuel-cell components subjected to a range of temperature and moisture conditions.
The research team, led by Iryna Zenyuk, a former Berkeley Lab postdoctoral researcher now at Tufts University, included scientists from Berkeley Lab’s Energy Storage and Distributed Resources Division and the Advanced Light Source (ALS), an X-ray source known as a synchrotron.
The ALS lets researchers image in 3-D at high resolution very quickly, allowing them to look inside working fuel cells in real-world conditions. The team created a test bed to mimic the temperature conditions of a working polymer-electrolyte fuel cell that is fed hydrogen and oxygen gases and produces water as a byproduct.
“The water management and temperature are critical,” said Adam Weber, a staff scientist in the Energy Technologies Area at Berkeley Lab and deputy director for a multi-lab fuel cell research effort, the Fuel Cell Consortium for Performance and Durability (FC-PAD).
The study has been published online in the journal Electrochimica Acta.
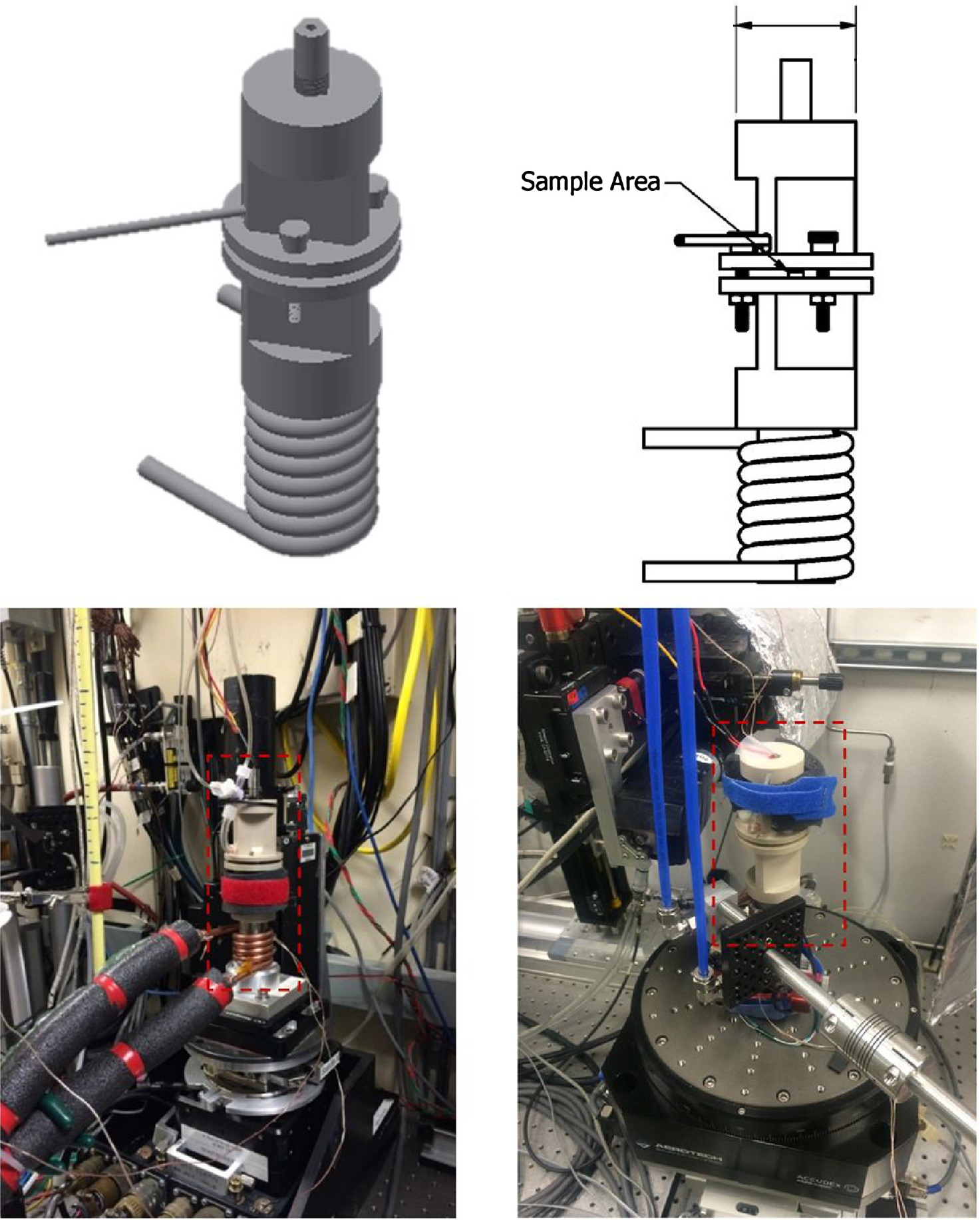
Temperature-controlled X-ray experiments on fuel-cell components were conducted at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (bottom left) and Argonne National Laboratory’s Advanced Photon Source (bottom right). The computer renderings (top) show the specialized sample holder, which included a heating element near the top and cooling coils at the base. (Credit: Berkeley Lab)
The research aims to find the right balance of humidity and temperature within the cell, and how water moves out of the cell.
Controlling how and where water vapor condenses in a cell, for example, is critical so that it doesn’t block incoming gases that facilitate chemical reactions.
“Water, if you don’t remove it, can cover the catalyst and prevent oxygen from reaching the reaction sites,” Weber said. But there has to be some humidity to ensure that the central membrane in the cell can efficiently conduct ions.
The research team used an X-ray technique known as micro X-ray computed tomography to record 3-D images of a sample fuel cell measuring about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter.
“The ALS lets us image in 3-D at high resolution very quickly, allowing us to look inside working fuel cells in real-world conditions,” said Dula Parkinson, a research scientist at the ALS who participated in the study.
The sample cell included thin carbon-fiber layers, known as gas-diffusion layers, which in a working cell sandwich a central polymer-based membrane coated with catalyst layers on both sides. These gas-diffusion layers help to distribute the reactant chemicals and then remove the products from the reactions.
Weber said that the study used materials that are relevant to commercial fuel cells. Some previous studies have explored how water wicks through and is shed from fuel-cell materials, and the new study added precise temperature controls and measurements to provide new insight on how water and temperature interact in these materials.
Complimentary experiments at the ALS and at Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source, a synchrotron that specializes in a different range of X-ray energies, provided detailed views of the water evaporation, condensation, and distribution in the cell during temperature changes.
“It took the ALS to explore the physics of this,” Weber said, “so we can compare this to theoretical models and eventually optimize the water management process and thus the cell performance,” Weber said.
The experiments focused on average temperatures ranging from about 95 to 122 degrees Fahrenheit, with temperature variations of 60 to 80 degrees (hotter to colder) within the cell. Measurements were taken over the course of about four hours. The results provided key information to validate water and heat models that detail fuel-cell function.
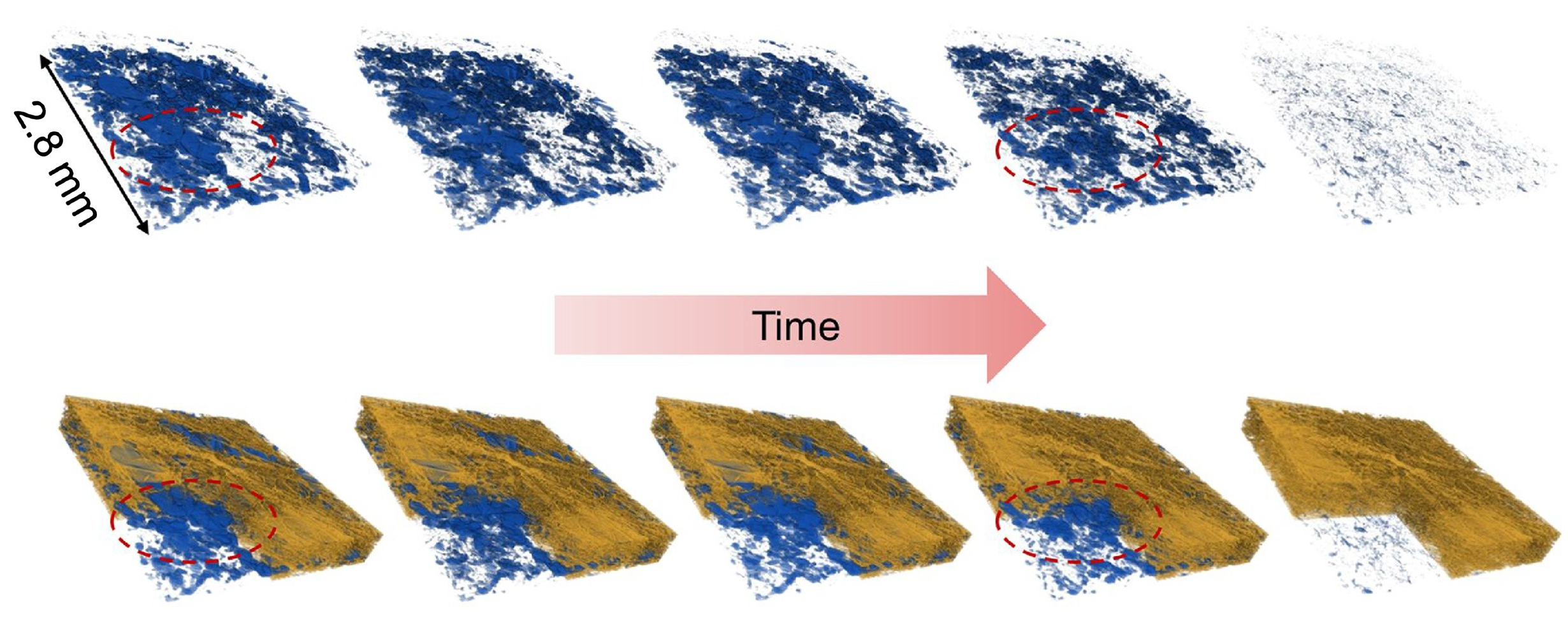
Water clusters in sample fuel-cell components shrink over time in this sequence of images, produced by a 3-D imaging technique known as micro X-ray computed tomography. The water clusters were contained in a fibrous membrane that was exposed to different temperatures. The mean temperature began at about 104 degrees Fahrenheit and was gradually increased to about 131 degrees Fahrenheit. The top side of the images was the hotter side of the sample, and the bottom of the images was the colder side. (Credit: Berkeley Lab)
This test cell included a hot side designed to show how water evaporates at the site of the chemical reactions, and a cooler side to show how water vapor condenses and drives the bulk of the water movement in the cell.
While the thermal conductivity of the carbon-fiber layers – their ability to transfer heat energy – decreased slightly as the moisture content declined, the study found that even the slightest degree of saturation produced nearly double the thermal conductivity of a completely dry carbon-fiber layer. Water evaporation within the cell appears to dramatically increase at about 120 degrees Fahrenheit, researchers found.
The experiments showed water distribution with millionths-of-a-meter precision, and suggested that water transport is largely driven by two processes: the operation of the fuel cell and the purging of water from the cell.
The study found that larger water clusters evaporate more rapidly than smaller clusters. The study also found that the shape of water clusters in the fuel cell tend to resemble flattened spheres, while voids imaged in the carbon-fiber layers tend to be somewhat football-shaped.
There are also some ongoing studies, Weber said, to use the X-ray-based imaging technique to look inside a full subscale fuel cell one section at a time.
“There are ways to stitch together the imaging so that you get a much larger field of view,” he said. This process is being evaluated as a way to find the origin of failure sites in cells through imaging before and after testing. A typical working subscale fuel cell measures around 50 square centimeters, he added.
Other researchers participating in this study were from Tufts University, Argonne National Laboratory, and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. The work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fuel Cell Technologies Office and Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, and the National Science Foundation.
The Advanced Light Source and the Advanced Photon Source are DOE Office of Science User Facilities that are open to visiting scientists from around the U.S. and world.
# # #
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel Prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.