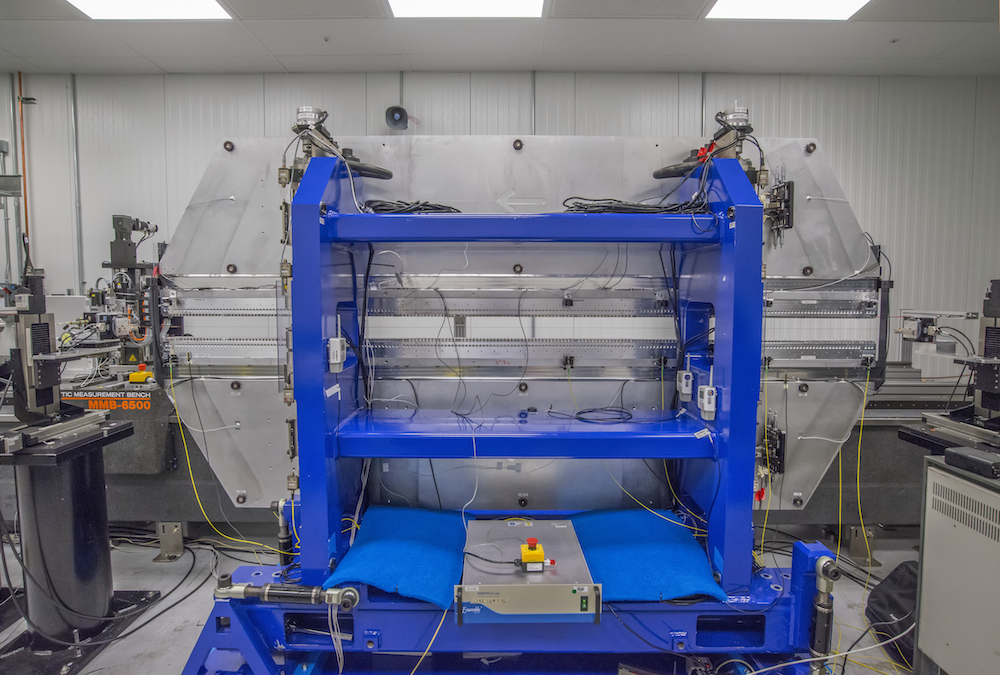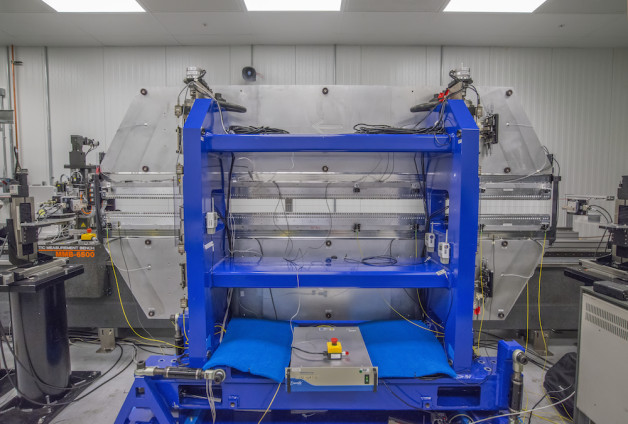
A prototype LCLS-II undulator, which is designed to wiggle electrons, causing them to emit brilliant X-ray light, undergoes magnetic measurements at Berkeley Lab. (Credit: Roy Kaltschmidt/Berkeley Lab)
X-ray free-electron lasers, first realized a decade ago, produce the brightest X-rays on the planet, and scientists tap into these unique X-rays to explore matter at the atomic scale and observe processes that occur in just quadrillionths of a second.
As the name suggests, an X-ray free-electron laser requires electrons—lots of them, and in very compact bunches. Those electron bunches are actually initiated by rapid-fire laser pulses produced by an electron “gun.” And to get those electrons to give up energy in the form of ultrabright X-ray light, they are wiggled in powerful, alternating magnetic fields in a device called an “undulator.”
Now, as part of a unique new X-ray laser project, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) are managing the development of a new breed of electron gun that provides a near-continuous stream of electron bunches, and new, highly tunable undulators.
This LCLS-II project, under construction at the DOE’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in Menlo Park, Calif., will add a second X-ray laser and a superconducting linear accelerator to the existing light source that will enable more experiments and brighter X-rays. Berkeley Lab’s Engineering Division and Accelerator Technology and Applied Physics Division are involved in the LCLS-II work.
This movie introduces LCLS-II, a future X-ray light source. It will generate over 8,000 times more light pulses per second than today’s most powerful X-ray laser, LCLS, and produce an almost continuous X-ray beam. (Credit: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory)
In addition to overseeing the design, development, testing and delivery of the LCLS-II undulators and electron gun, researchers at Berkeley Lab also have lead roles in control systems for parts of the superconducting accelerator and in modeling LCLS-II’s electron beam and X-ray production.
The making of an undulator
The new undulator segments for LCLS-II will come in two different forms: A chain of 21 lower-energy, or “soft” X-ray undulator segments, and a chain of 32 higher-energy or “hard” X-ray undulator segments.
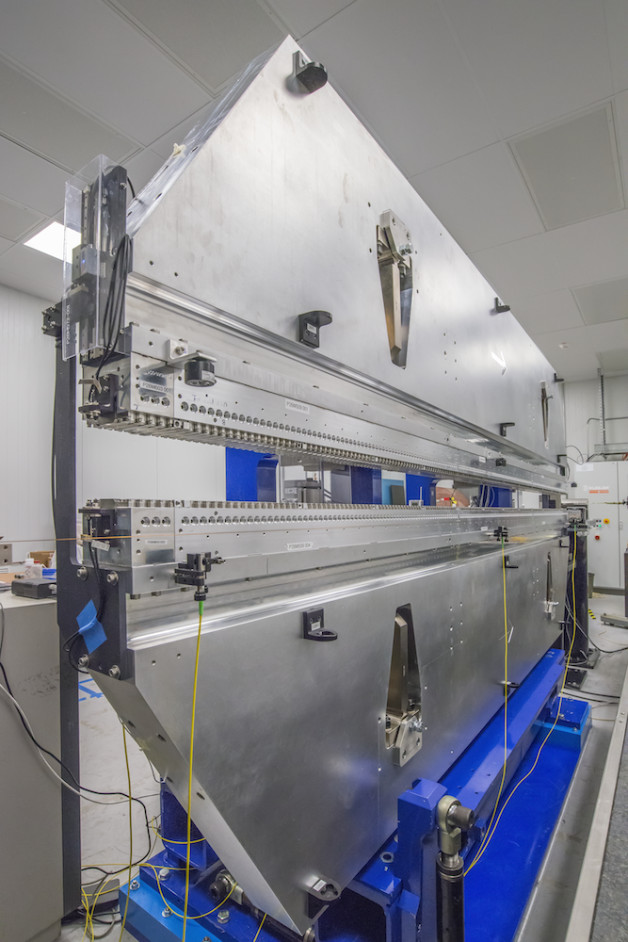

The powerful, toothlike rows of magnets (center) in this prototype device, called an undulator, can produce up to 7 tons of force. This undulator, designed for LCLS-II, an X-ray laser project, is needed to magnetically wiggle electrons, causing them to emit X-ray light. (Credit: Roy Kaltschmidt/Berkeley Lab)
Each undulator segment measures about 11 feet in length and weighs about 6.5 tons, with strong steel frames that are built to withstand incredible magnetic forces produced by hundreds of individually tested and adjusted magnets in opposing rows along their lengths. Each soft X-ray undulator segment will have 346 magnets and each hard X-ray segment will have 518 magnets.
“The magnetic forces are so strong—the system has to withstand about 7 tons of force,” said Matthaeus Leitner, a Berkeley Lab engineer who is managing the development effort for the LCLS-II undulators.
The rows of magnets in each segment can be moved closer together or farther apart to millionths-of-an-inch precision to fine-tune the energy of the X-ray pulses that form in their alternating magnetic fields. This adjustability, known as “variable gap,” is a new feature for LCLS-II.
“The undulator segments need to be designed for several hundred-thousand cycles of opening and closing,” Leitner said. “There are incredibly sturdy motors that overcome the magnetic forces.”
Berkeley Lab engineer Allan DeMello and three designers from the Lab’s mechanical engineering department have developed a series of prototypes for the variable-gap undulator segments.

A prototype LCLS-II undulator is loaded aboard a flatbed truck at Berkeley Lab in a practice delivery run. (Credit: Dawn Munson/Berkeley Lab)
A small-scale prototype completed in 2013 was followed by a full-size undulator segment that was successfully tested in the lab’s Undulator Measurement Facility, which precisely measures and tunes the magnetic specs. A pre-production soft X-ray undulator segment prototype is now in the works, and a new hard X-ray design—developed by Berkeley Lab based on an alternative approach originally devised at Argonne National Laboratory—will be tested later this year.
As the project moves forward, much of the production and assembly of the segments will be carried out by offsite vendors, said Dawn Munson, a Berkeley Lab mechanical engineer and technical representative for the LCLS-II project.
“This is a very exciting time—everything is going to happen really fast,” said Munson, who has been working on the LCLS-II project since 2010. “We’ve put in place a lot of specifications with the vendors and we have really good communications.”
The Berkeley Lab Undulator Measurement Facility will handle the tests on about one-third of the LCLS-II undulator segments, and SLAC will test the rest.
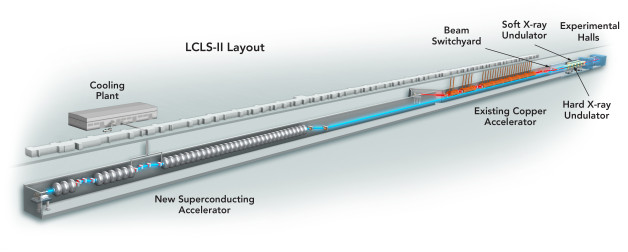
The future LCLS-II X-ray laser (blue, at left) is shown alongside the existing LCLS (red, at right). For LCLS-II, the first third of its copper accelerator will be replaced with a superconducting one, capable of creating up to 1 million X-ray flashes per second. The X-ray undulators are shown at right. (Credit: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory)
Erik Wallen, an engineer responsible for the magnetic measurements, said the facility is built like a “building within a building,” with specially designed lighting and power cabling to limit sources of electromagnetic noise and preserve the accuracy of its measurements. The measurements must account even for the effects of Earth’s magnetic field, he said.
Berkeley Lab researchers developed an innovative tuning mechanism for individual undulator magnets that uses stacks of tiny, hearing-aid-battery-sized magnets to compensate for very slight magnetic field defects. There are several other mechanisms, too, to individually hand-tune the fields of undulator magnets.
Diego Arbelaez, a Berkeley Lab mechanical engineer, developed a computer algorithm to optimize the performance of the undulator segments based on the tested properties of individual magnets.
“Magnets aren’t perfectly magnetized—they have some random errors. We started by simulating their behavior and developed methods for sorting and tuning,” Arbelaez said. The algorithms provide guidance for the position of individual magnets in each undulator segment. “We tried to handle the magnet-sorting as precisely as possible so when we install them we have as little tuning to do as possible,” he added.
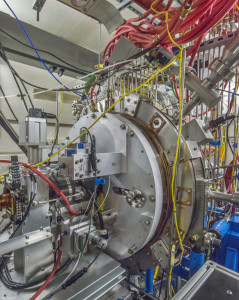
A Berkeley Lab-built predecessor to the electron “gun” that will produce electrons for a new, superconducting accelerator that will be a part of the LCLS-II project. Located at the future X-ray laser’s front end, it will produce bunches of electrons for the generation of X-ray pulses. (Credit: Roy Kaltschmidt/Berkeley Lab)
A new type of electron gun
The electron gun system for the LCLS-II superconducting linac, which springs from an R&D program begun at Berkeley Lab in 2009, should be ready for delivery to SLAC by the summer 2017, said Steve Virostek, a Berkeley Lab engineer responsible for its final design, fabrication and delivery.
Fernando Sannibale, a senior scientist who oversaw the development of a test electron gun and injector system known as APEX (Advanced Photo-injector EXperiment) and is also working on the LCLS-II system, said, “The new LCLS-II gun will be a slightly modified version of APEX—90 percent of the design will be the same.” The prototype LCLS-II injector’s cooling system has been redesigned to allow for a lower temperature when operating at ultrafast pulse rates, among other modifications.
The gun works by firing ultraviolet or visible-light laser pulses at a semiconductor surface known as a cathode. The laser light creates free bursts of electrons as it strikes the cathode. The injector will be remotely tunable to adjust the rate and other properties of LCLS-II pulses on demand.
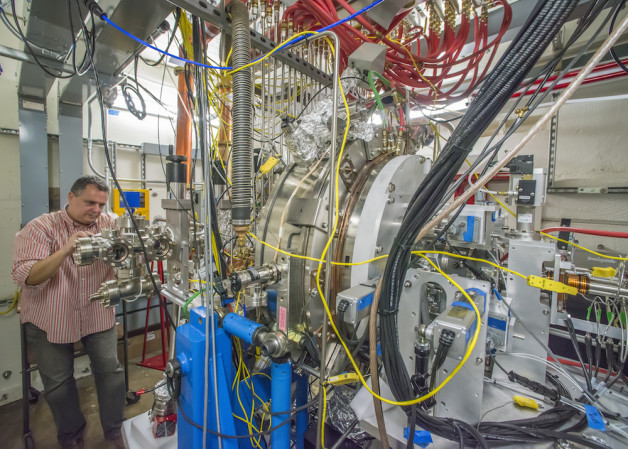
Berkeley Lab’s Fernando Sannibale inspects the APEX (Advanced Photoinjector Experiment) that has served as a test electron gun and injector system for LCLS-II. (Credit: Roy Kaltschmidt/Berkeley Lab)
The LCLS-II injector system, built of copper and stainless steel, will weigh about 1,500 pounds, and it must be assembled in a cleanroom to ensure that no contaminants can pass into the superconducting accelerator.
“The quality of the beam of the linear accelerator is really defined by the injector,” Sannibale said.
###
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.