Key Takeaways
- The Materials Project revolutionized the invention of new materials by creating them virtually, simulating their properties so researchers can focus on the most promising ones.
- Google DeepMind used information from the Materials Project to generate data on 2.2 million new compounds and their properties.
- The new GNoME dataset expands the Materials Project and may be valuable for researchers pursuing new materials, particularly for clean energy and environmental technologies.
New technology often calls for new materials – and with supercomputers and simulations, researchers don’t have to wade through inefficient guesswork to invent them from scratch.
The Materials Project, an open-access database founded at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) in 2011, computes the properties of both known and predicted materials. Researchers can focus on promising materials for future technologies – think lighter alloys that improve fuel economy in cars, more efficient solar cells to boost renewable energy, or faster transistors for the next generation of computers.
Now, Google DeepMind – Google’s artificial intelligence lab – is contributing nearly 400,000 new compounds to the Materials Project, expanding the amount of information researchers can draw upon. The dataset includes how the atoms of a material are arranged (the crystal structure) and how stable it is (formation energy).
“We have to create new materials if we are going to address the global environmental and climate challenges,” said Kristin Persson, the founder and director of the Materials Project at Berkeley Lab and a professor at UC Berkeley. “With innovation in materials, we can potentially develop recyclable plastics, harness waste energy, make better batteries, and build cheaper solar panels that last longer, among many other things.”
To generate the new data, Google DeepMind developed a deep learning tool called Graph Networks for Materials Exploration, or GNoME. Researchers trained GNoME using workflows and data that were developed over a decade by the Materials Project, and improved the GNoME algorithm through active learning. GNoME researchers ultimately produced 2.2 million crystal structures, including 380,000 that they are adding to the Materials Project and predict are stable, making them potentially useful in future technologies. The new results from Google DeepMind are published today in the journal Nature.
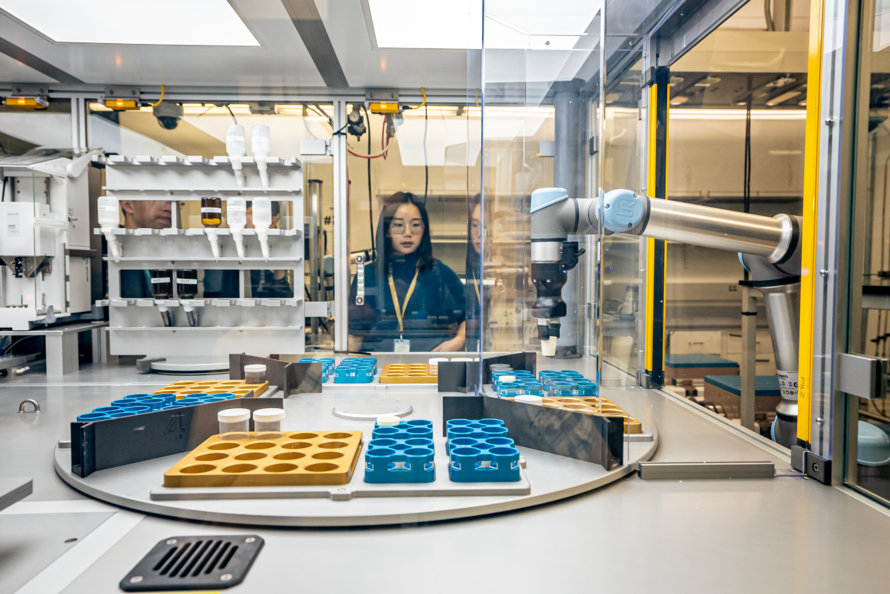
Some of the computations from GNoME were used alongside data from the Materials Project to test A-Lab, a facility at Berkeley Lab where artificial intelligence guides robots in making new materials. A-Lab’s first paper, also published today in Nature, showed that the autonomous lab can quickly discover novel materials with minimal human input.
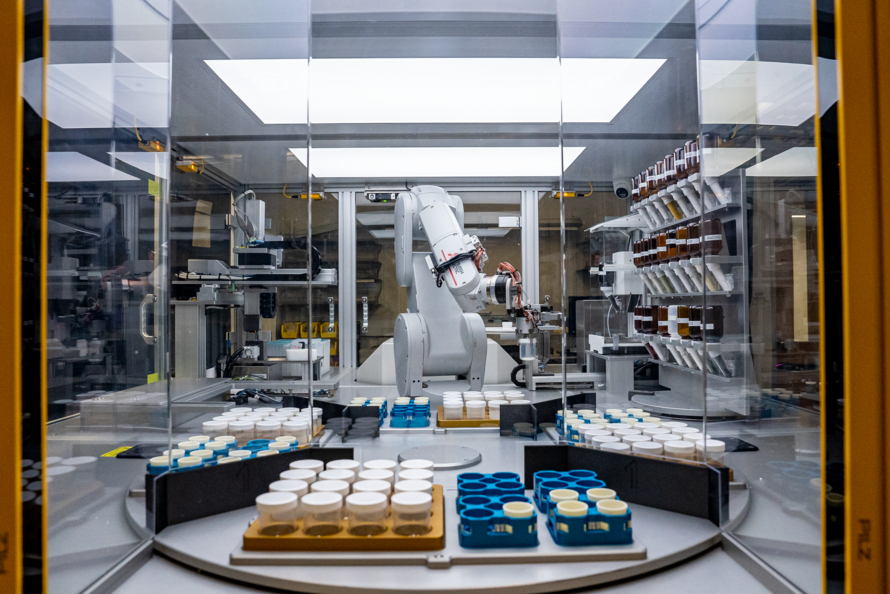

Robots guided by artificial intelligence created more than 40 new materials predicted by the Materials Project. Data from GNoME was used as an additional check on whether those predicted materials would be stable. (Credit: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab)
Over 17 days of independent operation, A-Lab successfully produced 41 new compounds out of an attempted 58 – a rate of more than two new materials per day. For comparison, it can take a human researcher months of guesswork and experimentation to create one new material, if they ever reach the desired material at all.
To make the novel compounds predicted by the Materials Project, A-Lab’s AI created new recipes by combing through scientific papers and using active learning to make adjustments. Data from the Materials Project and GNoME were used to evaluate the materials’ predicted stability.
“We had this staggering 71% success rate, and we already have a few ways to improve it,” said Gerd Ceder, the principal investigator for A-Lab and a scientist at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley. “We’ve shown that combining the theory and data side with automation has incredible results. We can make and test materials faster than ever before, and adding more data points to the Materials Project means we can make even smarter choices.”
The Materials Project is the most widely used open-access repository of information on inorganic materials in the world. The database holds millions of properties on hundreds of thousands of structures and molecules, information primarily processed at Berkeley Lab’s National Energy Research Science Computing Center. More than 400,000 people are registered as users of the site and, on average, more than four papers citing the Materials Project are published every day. The contribution from Google DeepMind is the biggest addition of structure-stability data from a group since the Materials Project began.
“We hope that the GNoME project will drive forward research into inorganic crystals,” said Ekin Dogus Cubuk, lead of Google DeepMind’s Materials Discovery team. “External researchers have already verified more than 736 of GNoME’s new materials through concurrent, independent physical experiments, demonstrating that our model’s discoveries can be realized in laboratories.”
The Materials Project is now processing the compounds from Google DeepMind and adding them into the online database. The new data will be freely available to researchers, and also feed into projects such as A-Lab that partner with the Materials Project.
“I’m really excited that people are using the work we’ve done to produce an unprecedented amount of materials information,” said Persson, who is also the director of Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry. “This is what I set out to do with the Materials Project: To not only make the data that I produced free and available to accelerate materials design for the world, but also to teach the world what computations can do for you. They can scan large spaces for new compounds and properties more efficiently and rapidly than experiments alone can.”
By following promising leads from data in the Materials Project over the past decade, researchers have experimentally confirmed useful properties in new materials across several areas. Some show potential for use:
- in carbon capture (pulling carbon dioxide from the atmosphere)
- as photocatalysts (materials that speed up chemical reactions in response to light and could be used to break down pollutants or generate hydrogen)
- as thermoelectrics (materials that could help harness waste heat and turn it into electrical power)
- as transparent conductors (which might be useful in solar cells, touch screens, or LEDs)
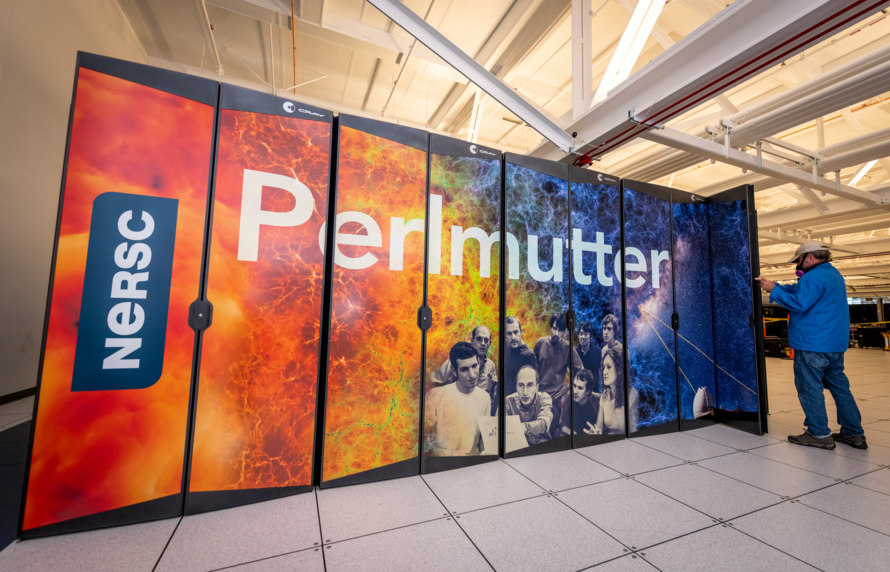

Many of the calculations for the Materials Project are performed on supercomputers at Berkeley Lab’s National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center. (Credit: Thor Swift/Berkeley Lab)
Of course, finding these prospective materials is only one of many steps to solving some of humanity’s big technology challenges.
“Making a material is not for the faint of heart,” Persson said. “It takes a long time to take a material from computation to commercialization. It has to have the right properties, work within devices, be able to scale, and have the right cost efficiency and performance. The goal with the Materials Project and facilities like A-Lab is to harness data, enable data-driven exploration, and ultimately give companies more viable shots on goal.”
###
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) is committed to delivering solutions for humankind through research in clean energy, a healthy planet, and discovery science. Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest problems are best addressed by teams, Berkeley Lab and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Researchers from around the world rely on the lab’s world-class scientific facilities for their own pioneering research. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.