Stars Forge Elements in a Way We’re Only Beginning to Understand
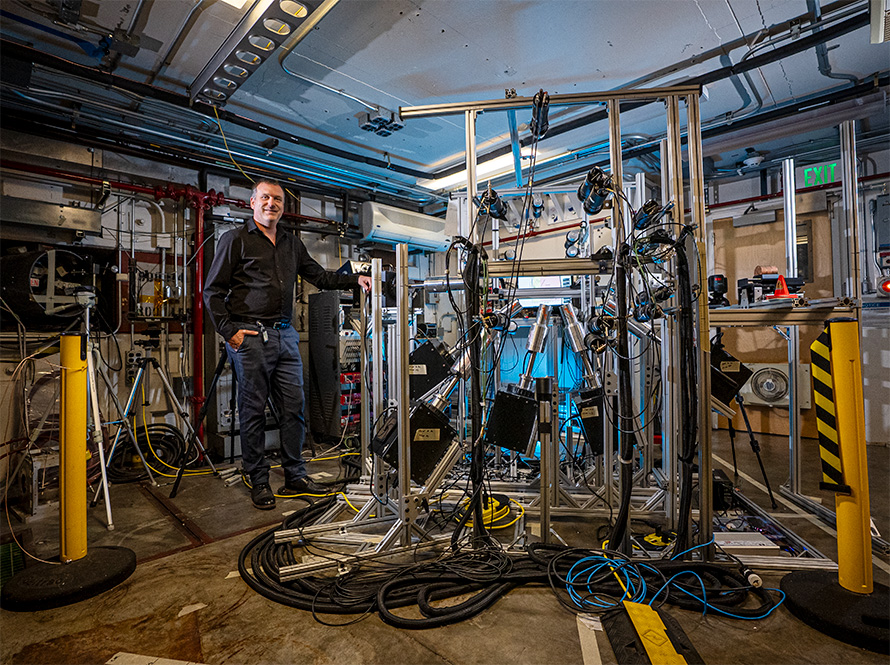
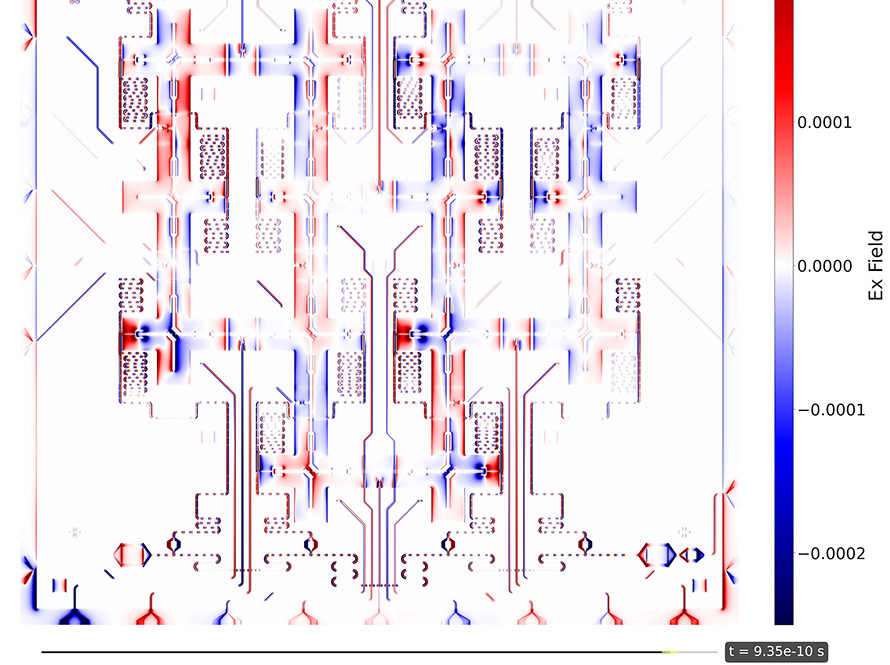
Unprecedented Perlmutter Simulation Details Quantum Chip
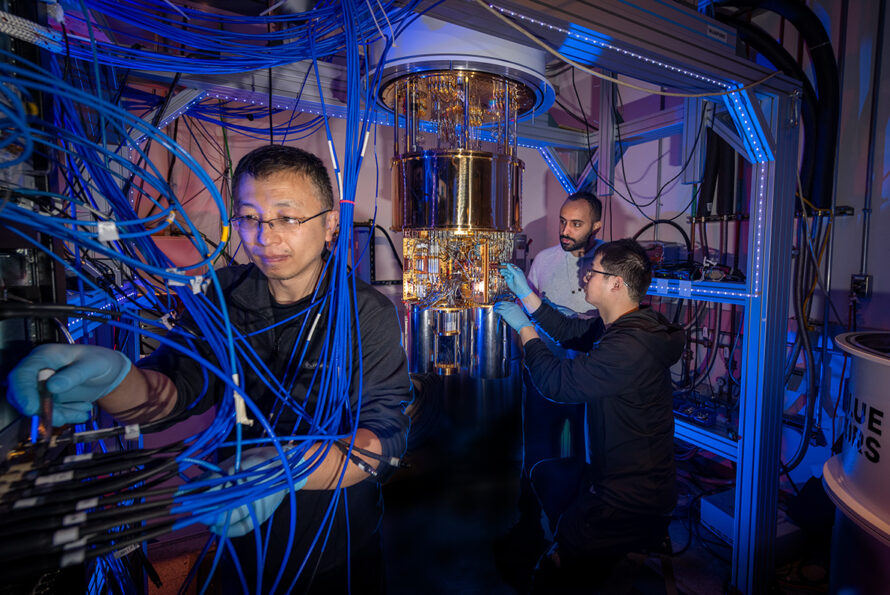
The Quantum Systems Accelerator Embarks on Next Five Years of Pioneering Quantum Technologies for Science
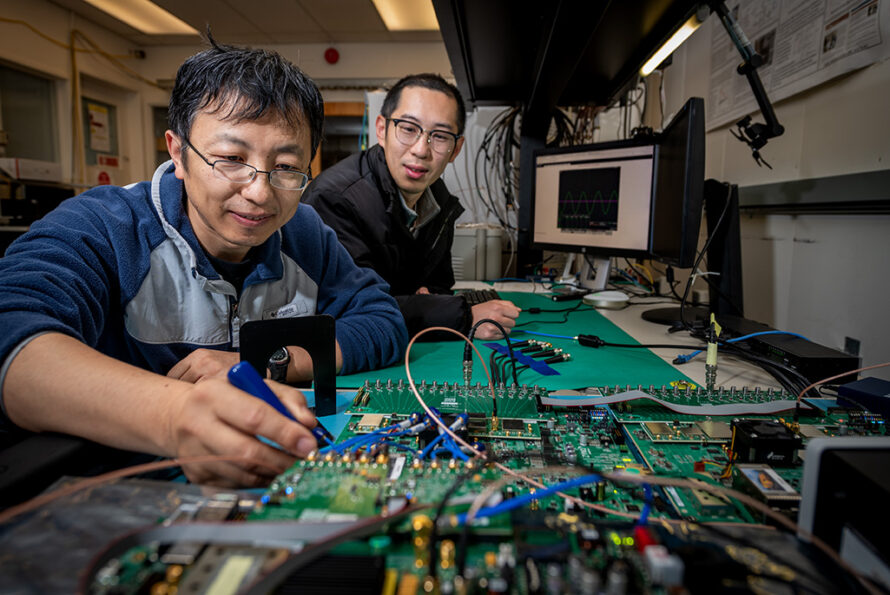
New Berkeley Lab and NVIDIA Partnership Integrates Quantum and AI Supercomputing for Next-Generation Research
Former Berkeley Lab Scientist John Clarke Wins 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics

More Signs of Phase-change ‘Turbulence’ in Nuclear Matter
Atomic Neighborhoods in Semiconductors Provide New Avenue for Designing Microelectronics
Electron Microscopy Reveals New Method to Make Exotic Metal Alloys
Early Research Demonstrated Novel Approach to Next-Generation Transistor Design
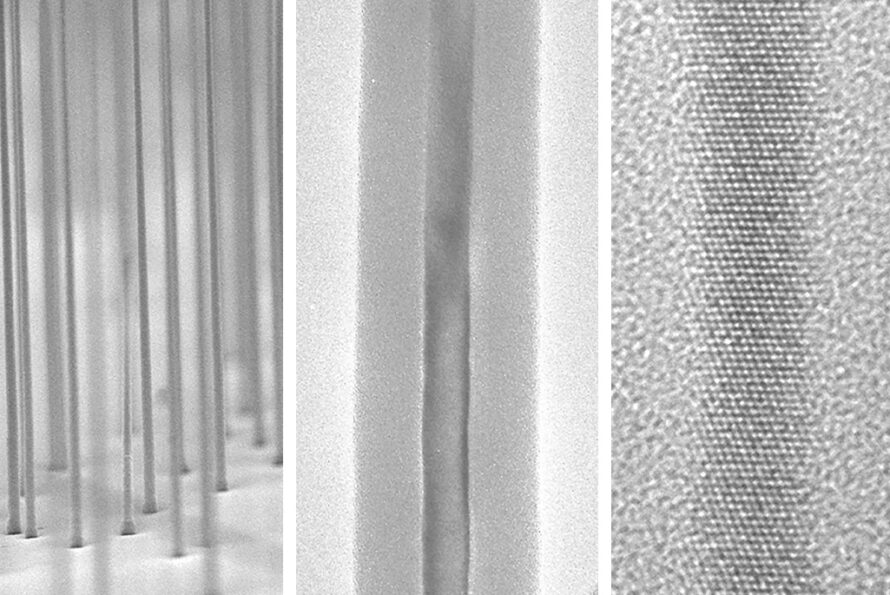
Optimized Materials in a Flash

How AI and Automation are Speeding Up Science and Discovery

Conventional vs. Enhanced Geothermal: What’s the Difference?
